Cholesteatoma is keratinizing squamous epithelium that present in the middle ear. In middle ear, it is line with different type of epithelium such as ciliated columnar, cuboidal & others. So, how can keratinizing squamous epithelium be present in the middle ear? Because of this, cholesteatoma was known as "skin in the wrong place". It is neither contain cholesterol crystal nor it is a tumor (-oma)
Cholesteatoma have 2 parts, that are :-
1. The matrix 2. A central white mass.
The Matrix : made up of keratinizing squamous epithelium which lies on a thin stroma of fibrous tissue.
Central White Mass : keratin debris which is the product of the matrix.
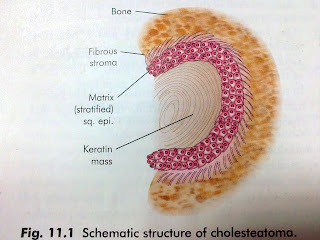 | |
| Based on one of the ENT book |
There are 3 types of Cholesteatoma :-
1. Congenital Cholesteatoma
2. Acquired, primary
3. Acquired, secondary
Congenital Cholesteatoma
Its arise from the embryonic epidermal cell & rest in the middle ear cleft / temporal bone.It usually occur at the middle ear, petrous apex & cerebellopontine angle.
For middle ear congenital cholesteatoma, it present as white mass behind an intact tympanic membrane.
One of the symptoms is hearing loss.
This usually occur in children.
Acquired, primary
There is no history of otitis media or a pre-existing perforation. So, it might be due to :-
- Invagination of Pars Flaccida - cause by persistence negative pressure in the attic
- Basal cell hyperplasia- cause by proliferation o basal cell of Pars Flaccida which induced by subclinical childhood infection.
- Squamous metaplasia - cause by metaplasia of normal pavement of the attic
there is already pre-existing perforation of Pars Tensa. this is happen may be due to :-
- Migration of squamous epithelium - cause by the migration of the keratinizing squamous epithelium from external auditory canal / outer surface of tympanic membrane to the middle ear through the perforation
- Metaplasia - caused by repeated metaplasia
Symptoms :-
Hearing loss, malodorous discharge, & pain
(also can be associate with polyps in the attic of middle ear / perforation of tympanic membrane)
Diagnosis :-
1. Otoscopy (to reveal collection of white debris)
2. Audiometric (to test the degree of hearing loss)
3. CT scan (to look for the size of the cholesteatoma & the structure that it already encroach)
Treatment :-
1. Mastoidectomy (to expose & eliminate the disease)
2. Tympanoplasty (to repair the tympanic membrane)
3. Ossiculoplasty ( to repair the ossicles)
*** Cholesteatoma have the property to destroy bone. It is because, it produce various enzymes, such as collegenase, acid phosphatase & proteolytic enzymes. Bone erosin can lead to several other complication.



No comments:
Post a Comment